Executive Summary:
In the thousands of years of human civilization, there have always been divisions. It is a sad fact that people are treated differently not because of their ability but because of their origin. This has lasted for all mankind history. The internet is the first-ever invention of mankind that disregards all differences of human beings meaning that every oneonline is treated as equal; an intelligent being irrespective of their status, race, colour, or origin.The internet’s main purpose is to unite minds together for communication, entertainment and the promotion of humanity. And thanks to the internet, we are able to traverse race, colour and origin in a space where intelligent and similar individuals/groups meet.
However, it would be naive to think that the internet does not have problems to overcome. The Internet has run into major setbacks such as the property value of IP address registration, the lack of regulations in the IP market and the dominance of large corporations. Furthermore, the slow transition from IPv4 to IPv6 and a lack of innovation within the internet community has caused the internet to stagnate.
These problems have plagued the internet community for years and is the motivation behind LARUS being at the forefront of implementing much needed changes in opening up access to the internet for the benefit of humanity.
That is why Hong Kong based LARUS, partners with firms worldwide to lease IPv4 addresses to millions of end-users worldwide, whilst also providing IPv6 training and education to the nurture the next generation of talent.
LARUS is motivated to create a better Internet for all
Creating a fairer internet for all – the history
The emergence of a global computer network and the intensification of our reliance upon it has prompted debate about openness and most significantly, equality and fairness.One of the key areas of debate has been internet governance. The internet used to be a computer network shared between universities. Its governance structure was never designed to counter a challenge to become the unity of the modern society.
IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) addresses are a fundamental constituent of communication over the Internet as we know it. An Ipv4 address enables every packet to reach its destination anywhere on the Internet. Publicly-routable Ipv4 address space is therefore required to interconnect Internet users with global digital services, such as online content.
There are a total of 4.3 Billion Ipv4 addresses on the planet. IP were once infinite when the Internet was small, but they became scarce once the Internet reaches every home on this planet, with each individual holding multiple devices that are connected to the Internet. Because of this and the exhaustion of Ipv4 addresses on the central free pool, the market for Ipv4 has been formed about a decade ago.
Regional Internet Registries
RIRs (Regional Internet Registries) were first created to distribute and register Internet number resources, such as IP addresses and autonomous system (AS) numbers. Such functions make it a vital cog in the running of the internet.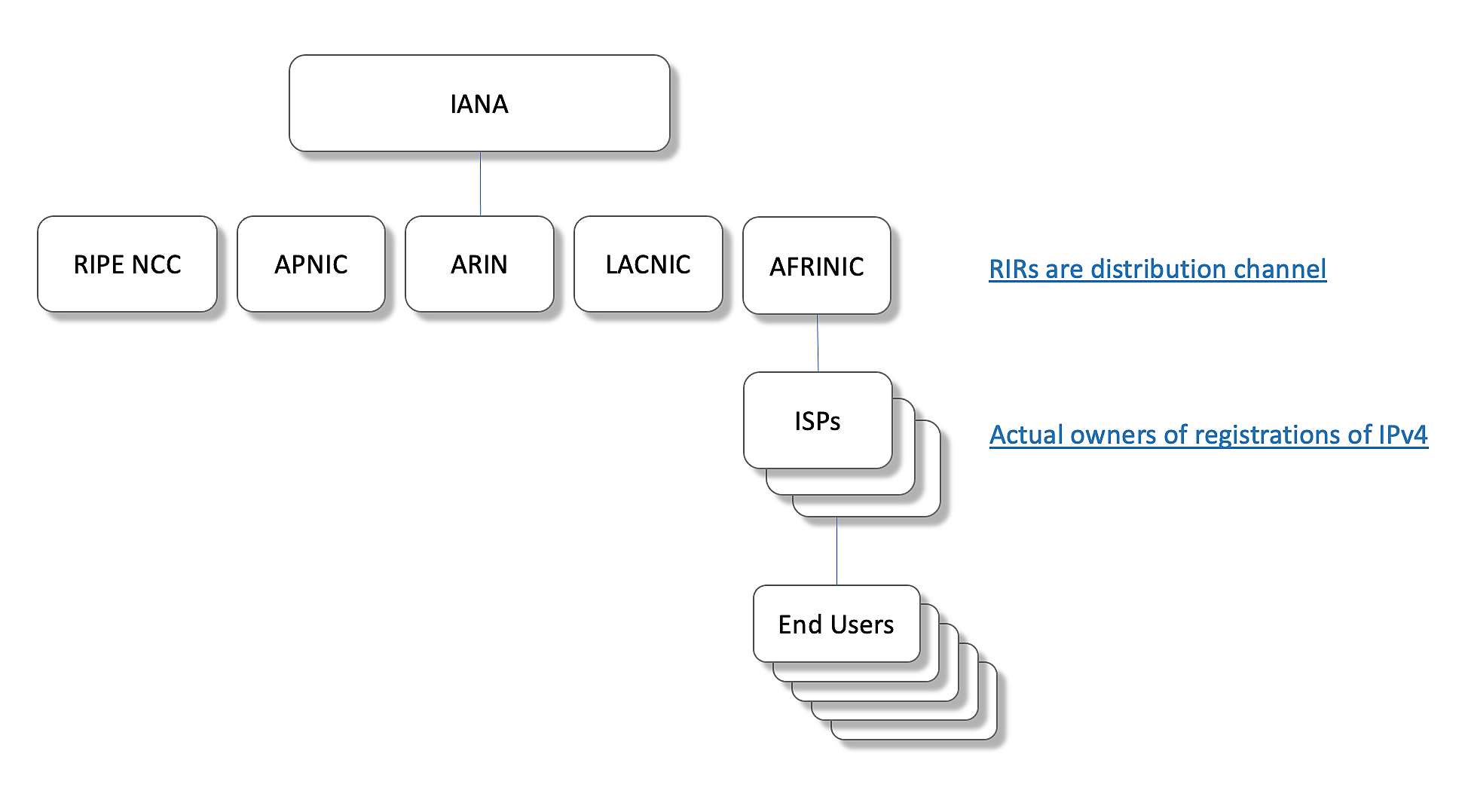 The IANA (Internet Assigned Number Authority) on the other hand, is responsible for Internet protocol, coordinating global IP addressing, symbols, numbering, media-type and DNS root zone management. One important thing to note is that Regional Internet registries are components of the Internet Number Registry System. So while the IANA delegates Internet resources to the RIR based on the accumulated technical need of RIR's customers, the RIRs in turn, follow their regional policies to delegate resources to those in need of the resources such as internet service providers and content providers, who further provide service to end users such as home and business.
The IANA (Internet Assigned Number Authority) on the other hand, is responsible for Internet protocol, coordinating global IP addressing, symbols, numbering, media-type and DNS root zone management. One important thing to note is that Regional Internet registries are components of the Internet Number Registry System. So while the IANA delegates Internet resources to the RIR based on the accumulated technical need of RIR's customers, the RIRs in turn, follow their regional policies to delegate resources to those in need of the resources such as internet service providers and content providers, who further provide service to end users such as home and business.
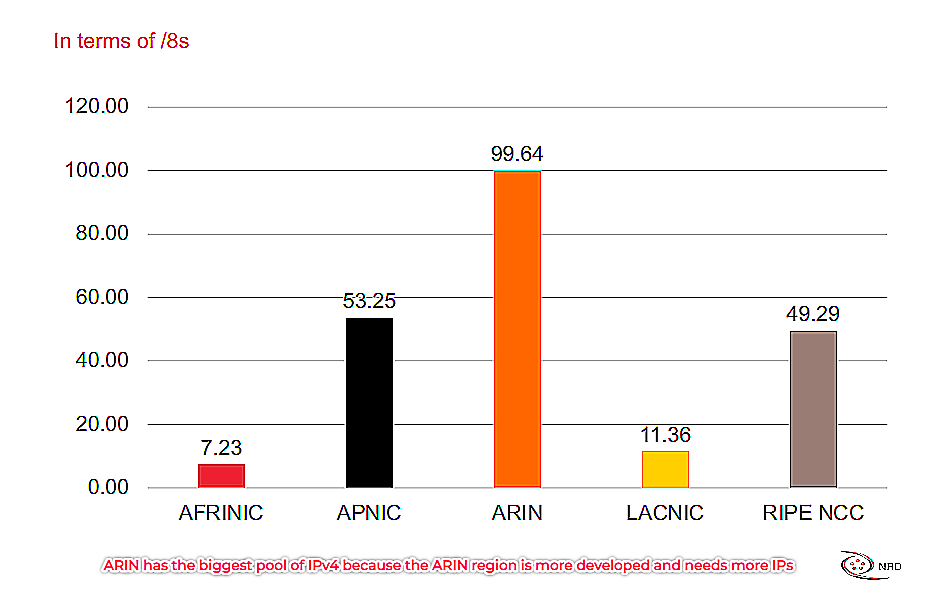
Figure 1: ARIN has the biggest pool of IPv4 as the region is more developed and needs more IPs
And for the past 30 years, IPs have been distributed under a fair scheme based on the technical needs of RIR customers. This scheme is fair and open; ensuring that no organization, people or race is denied access. Everyone has the right to connect to the internet, and everyone is equal, regardless of race, color or geographical location. Distribution should and must be fair. Registries such as AFRINIC and LACNIC, due to their lack of need from their customers (i.e., ISPs in the region), end up with the least amount of IP addresses to them. However, some international companies have nobly decided to apply IP addresses through those "minority" RIRs to boost those RIR's registration base and the number of internet resources they manage such as Cloud Innovation. However, due to the exhaustion of IPv4 on the central pool, a marketplace was formed tobecome the primary means for companies to access their growing need of internet resources. LARUS is one the first IPv4 management companies which manage highly valuable IPv4 registrations for IPv4 registration owners and distribute them in the market. This is similar to the role of RIRs in the old times - the difference is that LARUS's model is one of a free market model, with vendors including companies across the globe. Cloud Innovation is a notable example in which the firm had acquired a large of IPv4 registrations and handed them to LARUS for management.
Figure 2: IPv4 addresses have plummeted since its conception in 1969
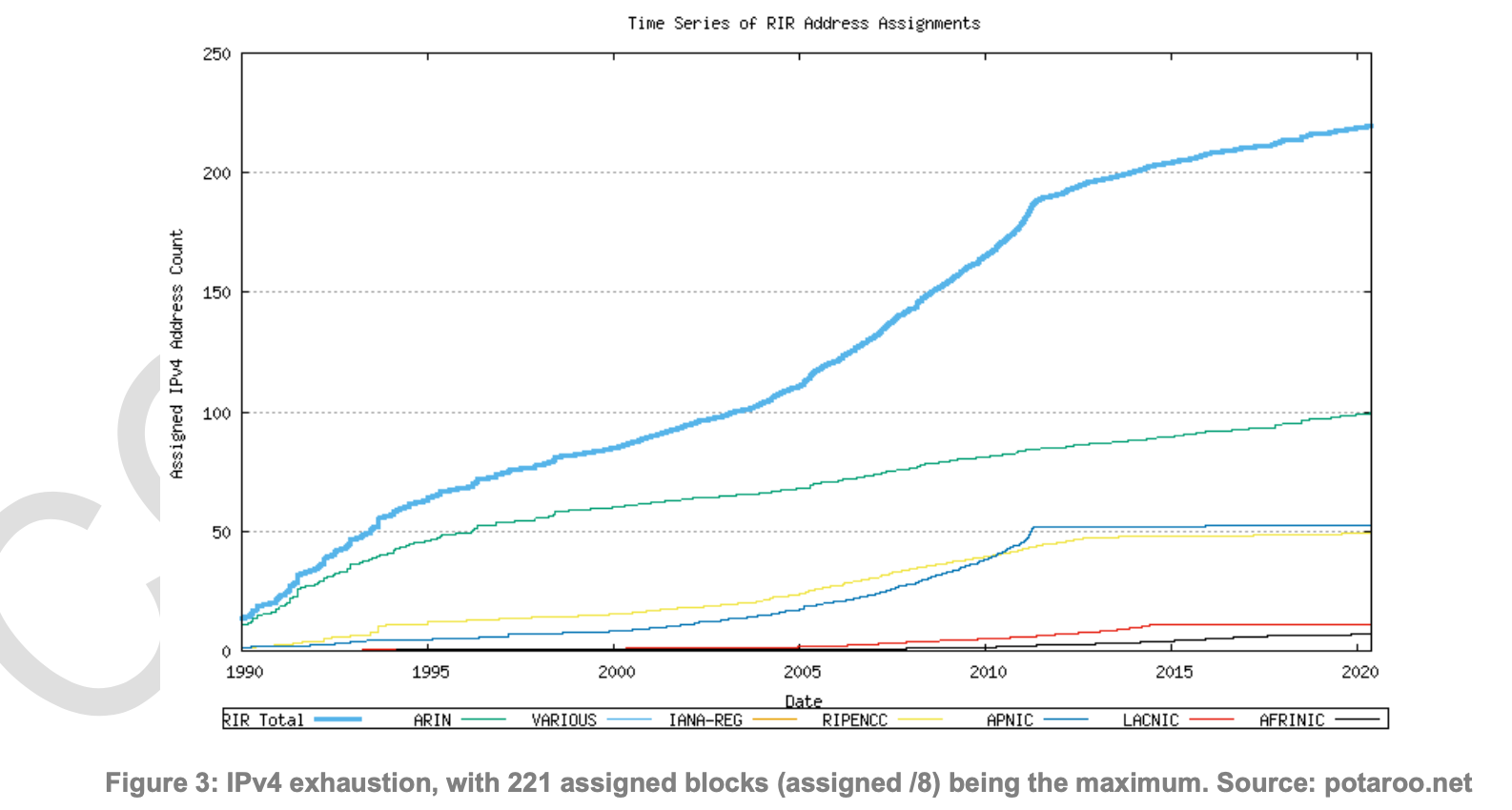 However, because there are no more addresses from IANA as IPs are exhausted, RIRs that once used to be both distribution channels and bookkeepers now should only carry the role of the "bookkeeper", while the distribution channels should be taken over by the market. However, this necessary transition is not entirely realized because of the reluctance and resistance of RIRs in accepting this change.
However, because there are no more addresses from IANA as IPs are exhausted, RIRs that once used to be both distribution channels and bookkeepers now should only carry the role of the "bookkeeper", while the distribution channels should be taken over by the market. However, this necessary transition is not entirely realized because of the reluctance and resistance of RIRs in accepting this change.
IP address registration and the lack of regulations
Created in 1980, IPv4 stands for Internet Protocol version 4 and it is what allows users to connect to the internet. Whenever a device accesses the Internet, it is assigned a unique, numerical IP address such as 8.8.8.8. Every internet user,whether its commercial, or home, has a unique IP address. The IPv4 market has seemingly been functioning properly for a long time, however, a problem remained: the lack of recognizing IPv4 property values. Based on NRO EC Oct 2021 Teleconference's minutes, the RIRs do not yet recognize the property ownership of IPv4 registration: “IP addresses are not property. The right to IP addresses is the right to registration of IP addresses, which comes with exclusive rights to use and to transfer them, based on and subject to a contractual relationship between the right holder and the relevant RIR. The right to registration of IP addresses may be eligible to seizure or some form of precautionary measure in civil proceedings, subject to limitations of the contractual relationship between the right holder and the relevant RIR.” (Source: https://www.nro.net/wp-content/uploads/2021-October-193AMinutesNROECTeleconference.pdf) Per the NRO (Number Resource Organization), the property rights of IPv4 addresses is not recognized by RIR. This is because the RIRs haven't transitioned from their role as distributors to becoming only bookkeepers. This lack of recognition of IPv4's property rights poses a serious threat to the stability of the IP market as well as that of the Internet itself, as companies face the danger of losing their IP addresses. This will directly affect end-users' connectivity. For any commodity market to function, recognition of the property value of the commodity is extremely important - it is the very foundation, The registration of IPv4 IP address on a global unique registration database clearly has its commercial value, and such commercial value today is valued over 200 billion USD worldwide (50 USD per IPv4 address with 4.3billion total number of IPv4 on the planet), and billions dollar of the transaction have been done for the past decades. RIRs being the NGO without any court power, should not have rights to define a property or even own that property in the society. Hence, having RIRs and their very limited community to decide on the faith of such a vast amount of value of asset seems unreasonable. We believe government and power of court should be brought inside into this in order to regulate, decide, just like any other tradeable commodity, in this society, who it belongs and how it is being traded fairly across the globe.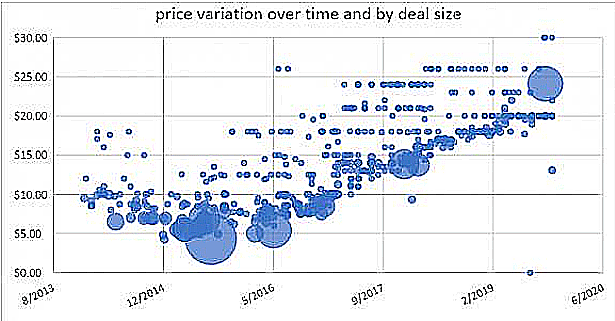
Figure 4: The price of IPv4 addresses over time
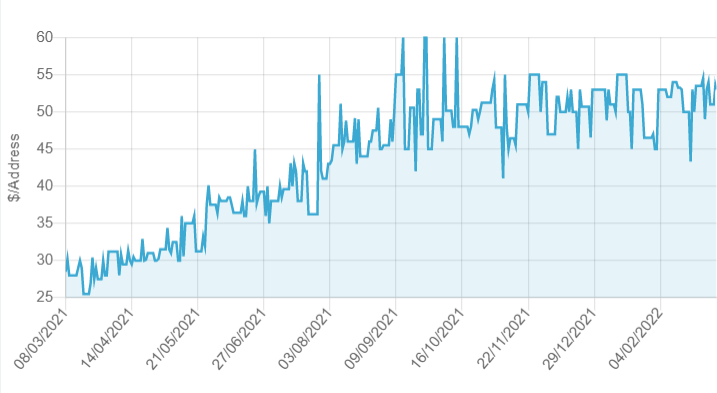
Figure 5: The sale of IPv4 addresses spiked in September and October 2021
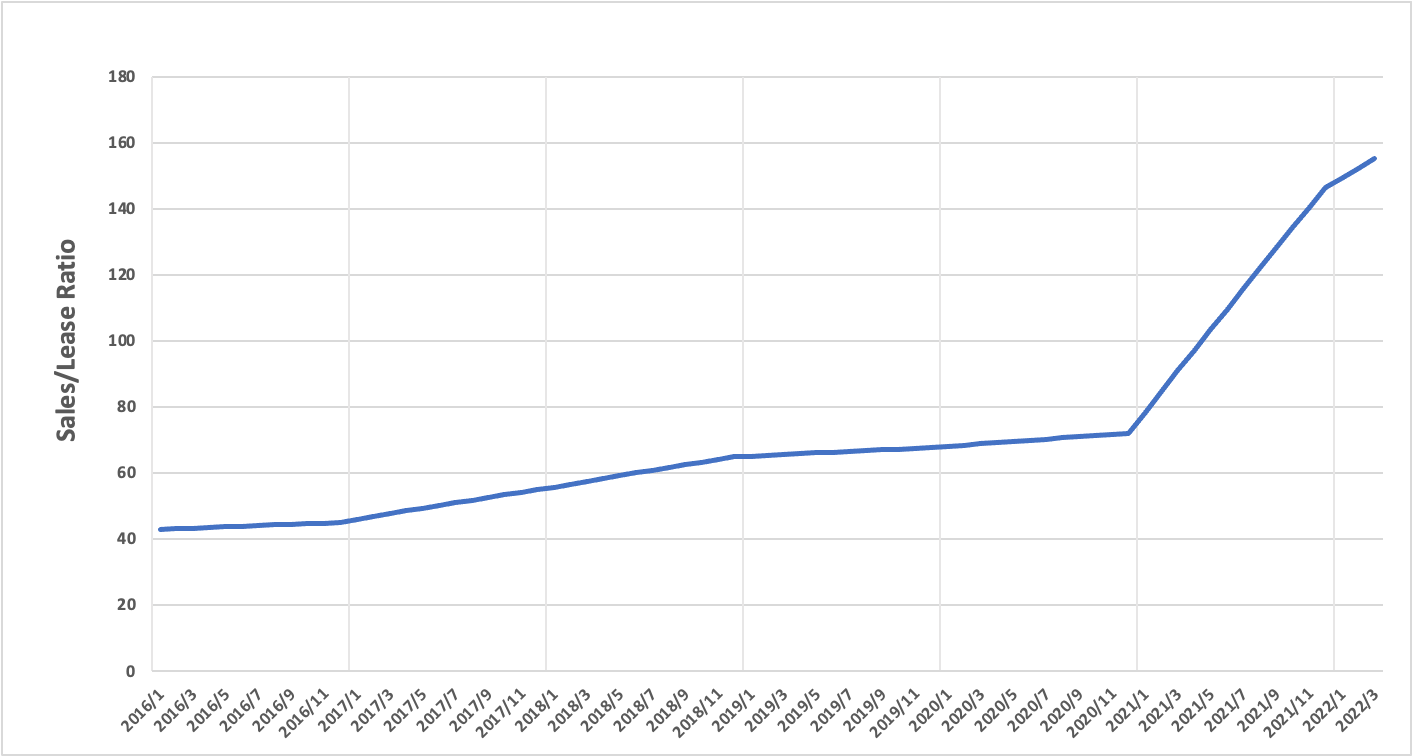
Figure 6: IPv4 Sales to Lease Price Ratio keeps rising from 2016 until March 2022
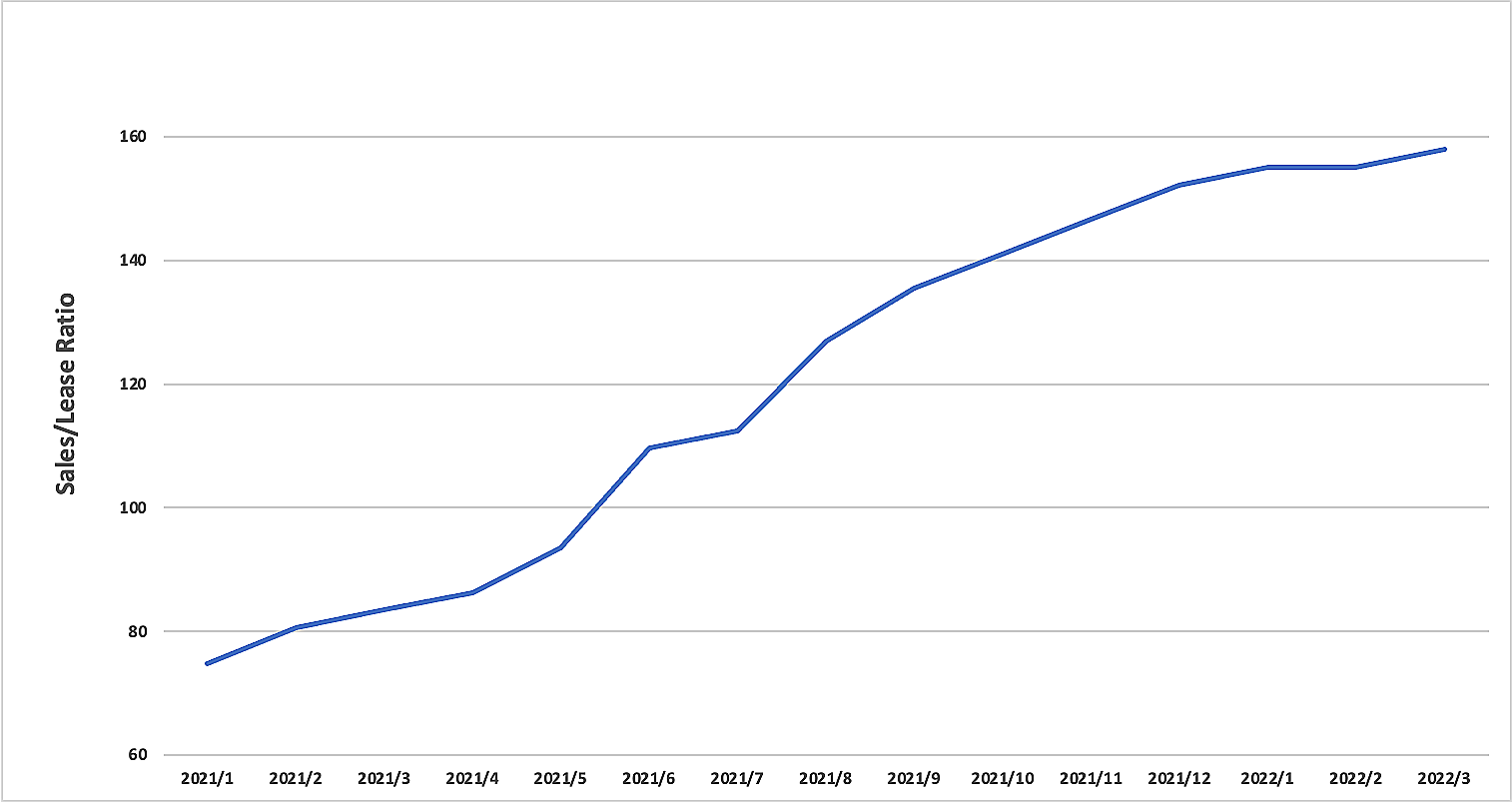
Figure 7: IPv4 Sales to Lease Price Ratio spiked from Jan 2021 until March 2022
The bubble of IPv4 market and dominance of major players
IPv4 address today represents almost 100% of the Internet. This is because, without IP addresses, one cannot access the Internet. Due to its limited supply and the fact that telecoms depend on it to survive, it is natural that the largest companies on planet earth are stocking IPv4 addresses as an insurance policy against an uncertain future in which IPv6 might or might not be fully implemented. This drives the bubble of the market, the buy/sell ratio of IPv4 market, just like any bubble real estate market, has been going at a crazy rate, as longs in the graph, it has jumped from 48-month rental to 156-month rental price equal to purchase price of IPv4 IP address. Due to this bubble and the very fact, there is no central free pool for businesses. The leasing market has become the only source for small-to-medium-size players to obtain IP for their businesses to future grow their business.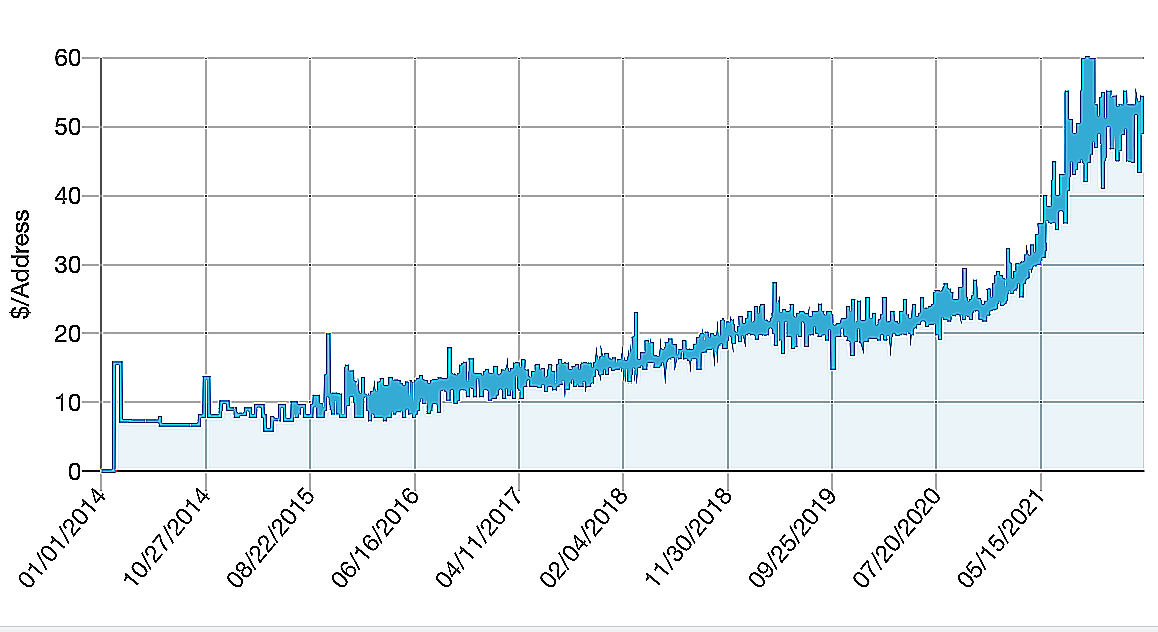
Figure 8: The price of IPv4 Sales continues to surge
The IPv4 leasing market
Leasing has become the preferred method of acquiring IPv4 addresses that are needed. The leasing market gives SMEs hope and a chance of being able to afford IP addresses so they can connect their end users, making sure that internet access is not provided by large telecoms and cloud providers but also by every new and innovative player. Embracing this new normal is the one way of ensuring the Internet is enjoyed by everyone. The Internet was created for the whole world to use - it was founded on the principle of fairness and openness. The leasing of IPv4 addresses has encountered policy challenges from the RIR community. Some have viewed the leasing of IPv4 addresses as the next-level evil of capitalism. In fact, it is merely an alternative solution. Like many young people have to rely on renting when they first arrive in a big city, the Internet today relies on leasing solution providers such as LARUS and cloud innovation for their affordable and less-capital intensive solutions. Like no housing market would forbid leasing and only embrace buy and sell, the discussion among leasing vs. buy/sell market has been rather intense, especially since cloud innovation's suite with AFRINIC came to light in 2021, Cloud Innovation. LARUS has been providing and leasing IPv4 addresses to hundreds of millions of end-users worldwide. In fact, by applying IP addresses in Africa, Cloud Innovation brings IPs to AFRINIC. LARUS leases its resources instead of selling them for instant profit also immensely benefits small-to-medium size players in all underdeveloped nations, providing internet access to hundreds of millions of people - who may otherwise not be able to access the Internet.The importance of the reality
We need policymakers from the RIRs government to recognize the reality of the IPv4 market and make it functional, transparent, fair to all players in the market for the healthy development of the very foundation of the Internet. We need to remove all obstacles - policy, legal, and emotional from this market, for all humankind to have fair, easy access to the very thing that units us.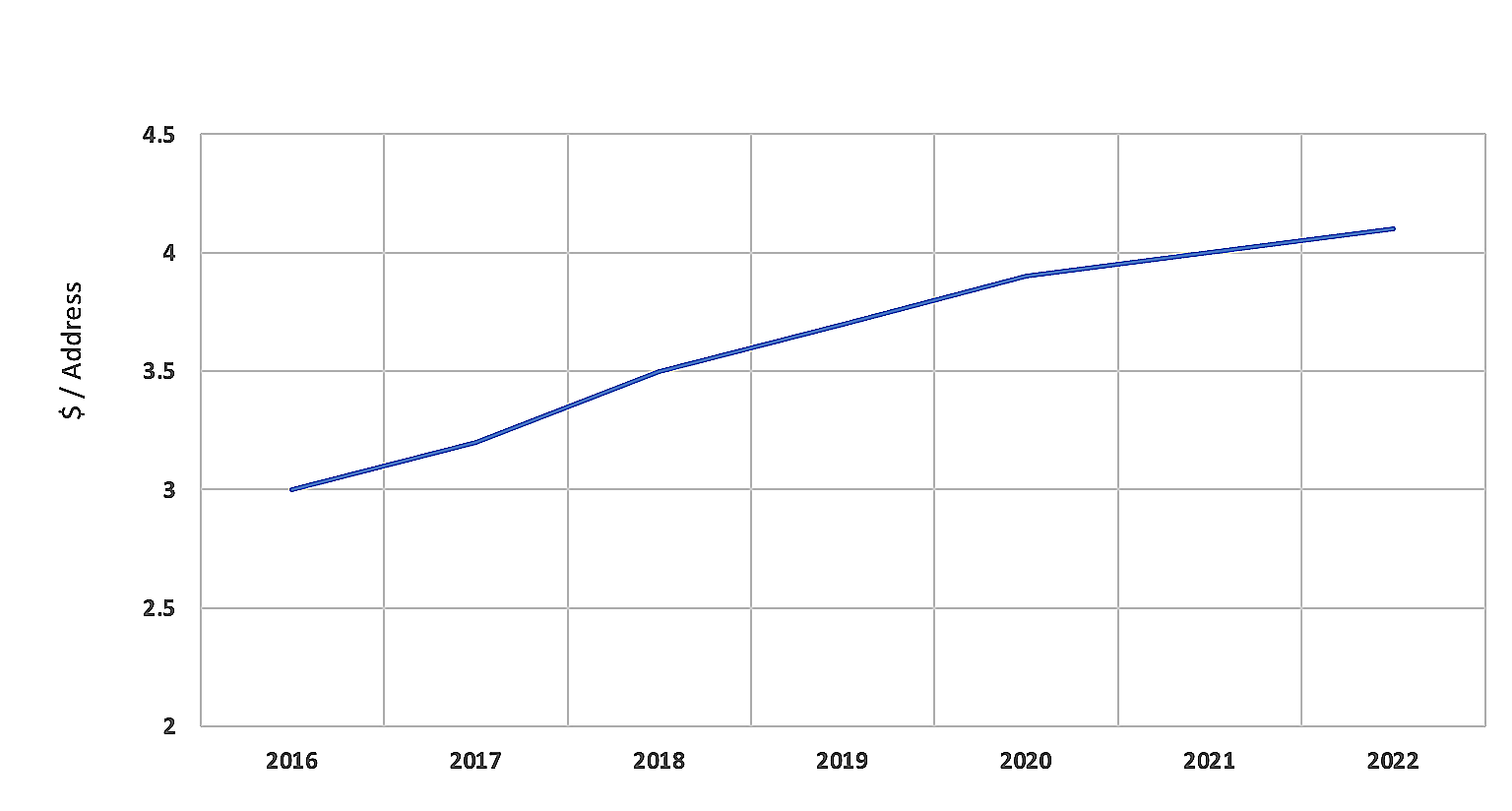
Figure 9: The lease price of IPv4 has grown at a much steadier pace
The Transition from IPv4 to IPv6
The growth of the internet proved that the world needed more IP addresses. And in 1998, IPv6 was created as the successor to IPv4. IPv6 uses 128-bit addressing to support approximately 3.4 x 10^38 unique IP addresses. This was created to ensure that when IPv4 addresses ultimately run out, the world will still have enough IP addresses for internet devices to expand for a long time. The deployment of IPv6 was considered important to the long-term growth and future sustainability of the Internet. Unfortunately, this hasn’t been the case. Because although IPv6 has been around for over 20 years; it has remained the "new, upcoming" technology without any real-life adoption. So while IPv4 might be considered an old technology, IPv6 has clearly shown its incompetence in becoming a worldwide accepted replacement solution. Due to the lack of innovation and participation of youth in the business, after 20 years of rather an unsuccessful adoption of IPv6, IPv6 is still the only visible solution to solve the problem of IPv4 shortage. This transition started around 20 years ago, and it is still very much at its earlier stage. There are few world leaders in this area of business to decide to lead this transition. LARUS provides full, one-stop IPv6 training and transition solutions. We aim to accelerate the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 while there is no visible new solution on the horizon. The future of the internet very much depends on innovation but is also prepared for continuity; the internet is so vital towards the human race that we can’t take the chance to let it fail.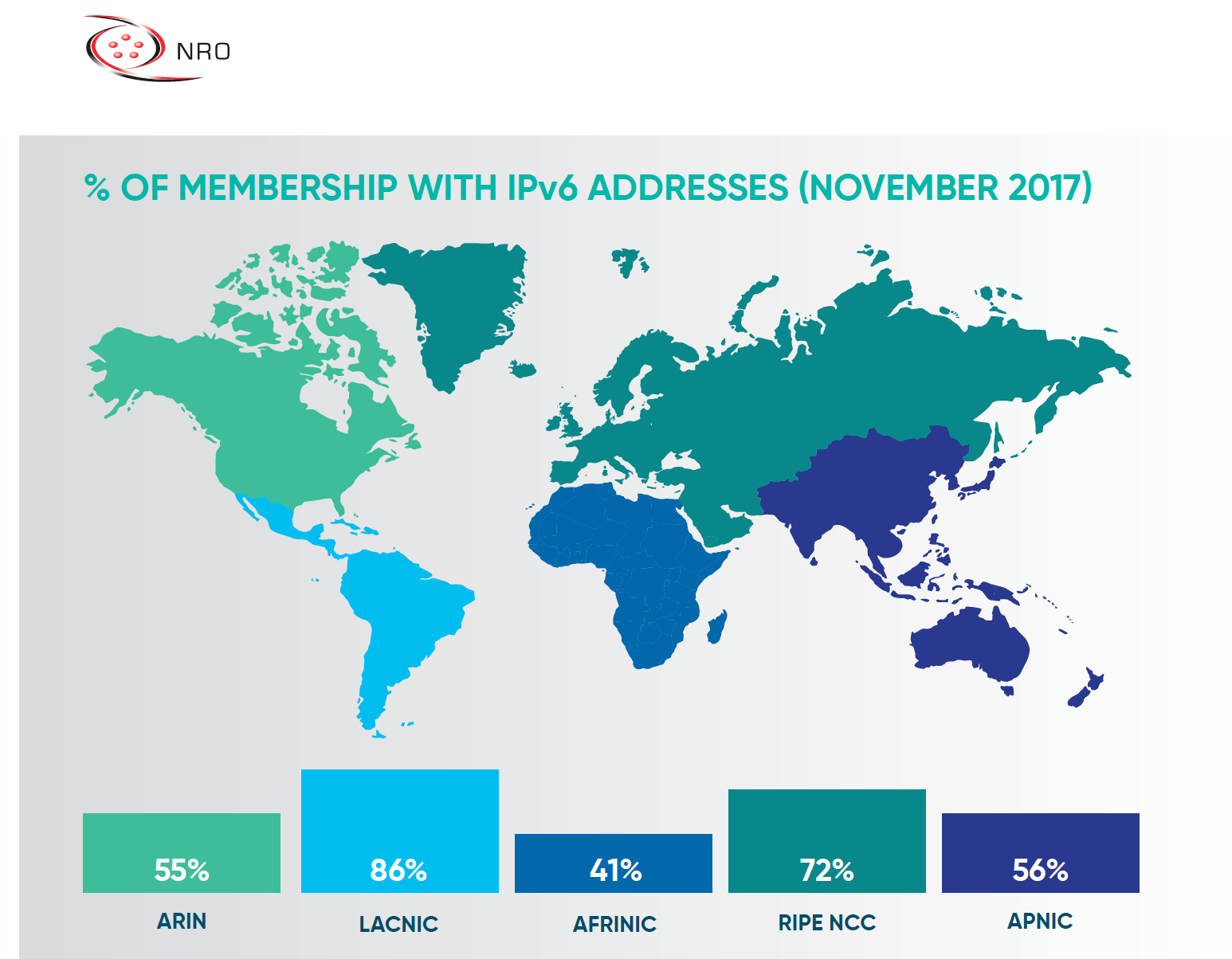
The latest research conducted by NRO shows that the average membership with IPv6 addresses is still low, with 3 out of the 5 regions only have around 50% membership. LACNIC and RIPE regions are relatively higher but there is still a lot to go before full adoption of IPv6 across the globe. The leasing market of IPv4 addresses has become even more important now than ever. SMEs cannot afford to wait for years while IPv6 is still not widely adopted. IPv4 is still essential to access the Internet. As a result, the leasing market has proven to be invaluable to these SMEs. At a reasonable price, they can lease IPv4 addresses without breaking the bank or waiting too long.
The need for youth and innovation
For over 20 years, IPv6 has been recognized as the "technology" of the future. This technology was launched 20 years ago, and it is quite disheartening that it's taken this long for little real progress has been made in terms of replacing IPv4 and creating an Internet with infinite possibility for expansion. According to ICANN Age Diversity and Participation Survey Report in 2019, it is shown that Respondents under 50 are less likely (than respondents 50 and older) to say they have more often felt included than excluded, with the percentage of 40% and 49%, respectively). Source: ICANN Age Diversity and Participation Survey Report, 2019. Also, the report indicates that respondents below 35 years old tend to feel disadvantaged because of their age.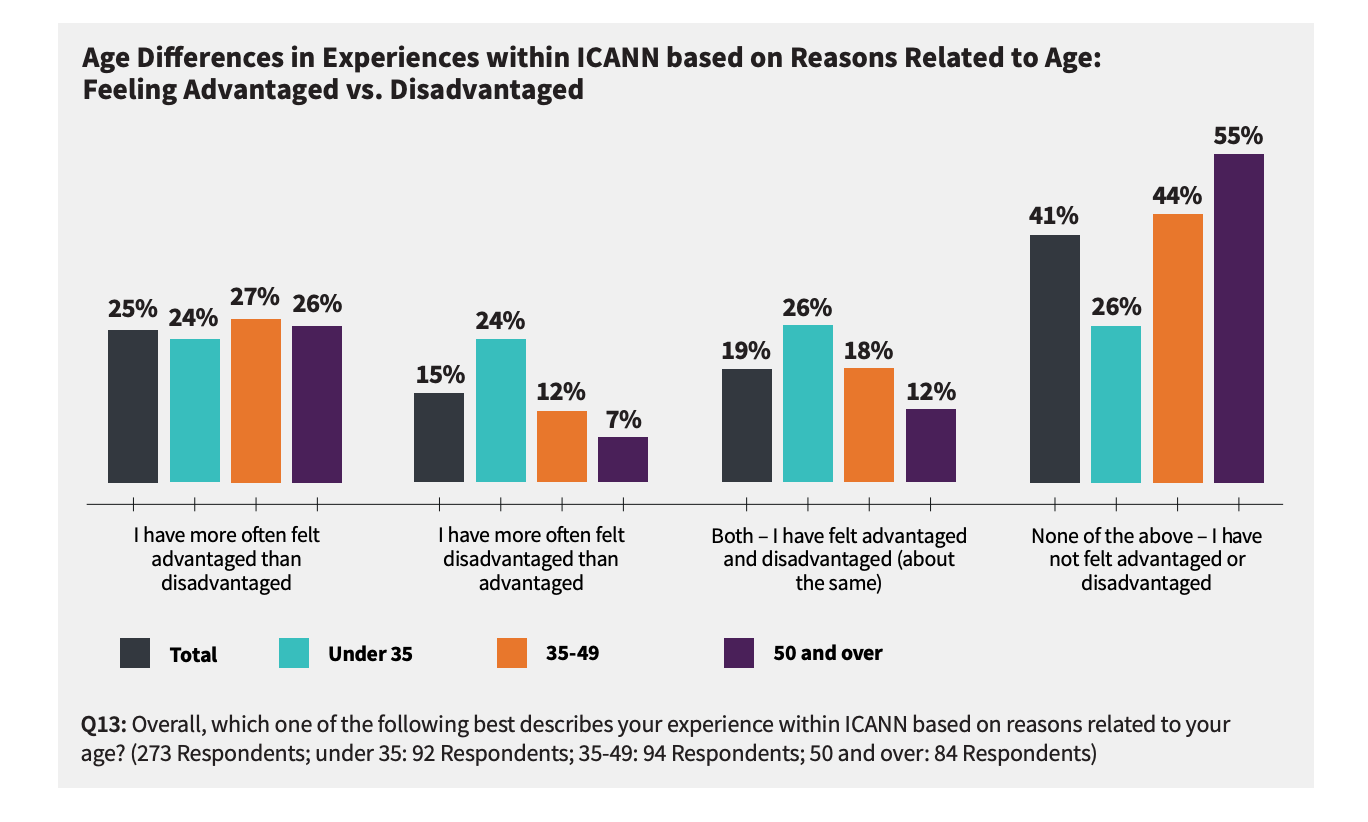
It is also more likely for them to feel ageism in ICANN events.
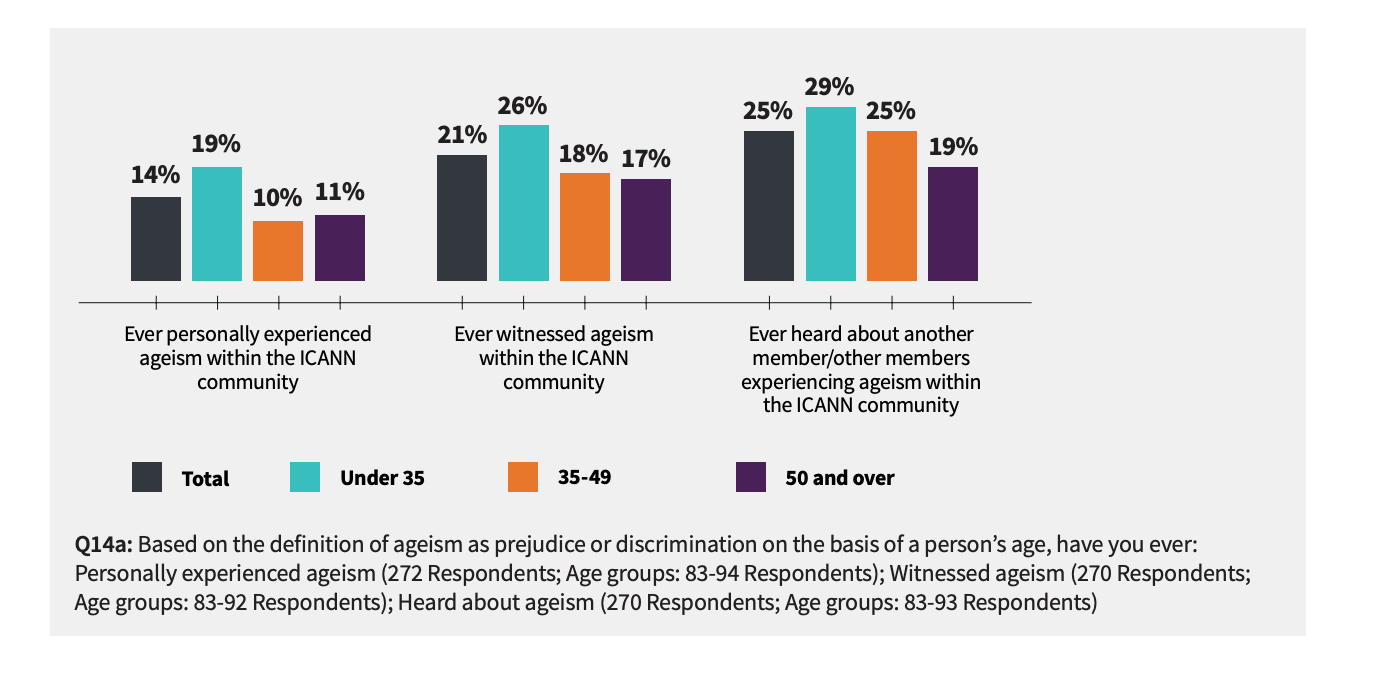 At LARUS we believe that innovation is the key to the answer. There is very little creativity in this industry for the past 30 years because we lack young people with the passion and the energy willing to bring much-needed change. For decades, besides the IPv6 which does not make any real impact despite it was invented 20 years ago, there hasn't been much breakthrough in terms of innovative technology and advancements within the foundation of the Internet. The foundation of the Internet is full of minor amendments and enhancements from old minds that are reluctant to embrace newness and lack the creativity needed to take the Internet to the next level. There needs to be a support for young talents for innovation to take place.
A lack of young people and drive has led to the failure to launch IPv6. It is not hard to find that recent RIR meetings have been attended solely by the same group of elderly professionals who have been in this industry for decades. While their contribution to the Internet is tremendous, it is also important for us to move forward by bringing in innovative and transformative ideas. We definitely need more energy in this industry.
Indeed, the Internet infrastructure industry may not be as profitable as the application business of the Internet, such as application and cryptocurrency. Young talents tend to go into these sectors for a better living. Meanwhile, as the Internet Infrastructure industry is still seemingly occupied by the "older professionals," this makes it even harder for young talents to enter this industry. Many young people are not even aware of the importance of Internet infrastructure, and relevant training and resources are limited. It is thus crucial for this industry to be innovative and to get rid of the image of being controlled by the "older folks" as a means to move forward.
LARUS understands the necessity of IPv6 as well as the importance of nurturing young talents. Along with the other firms, we provide IPv6 training and education. Furthermore, the LARUS Foundation, a government-recognized NGO founded in 2019 to promote education in Internet Governance and nurture the next generation of talents for a better Internet, has helped this cause. To date, we have educated over 10,000 students, and we hope to educate more in the years to come.
At LARUS we believe that innovation is the key to the answer. There is very little creativity in this industry for the past 30 years because we lack young people with the passion and the energy willing to bring much-needed change. For decades, besides the IPv6 which does not make any real impact despite it was invented 20 years ago, there hasn't been much breakthrough in terms of innovative technology and advancements within the foundation of the Internet. The foundation of the Internet is full of minor amendments and enhancements from old minds that are reluctant to embrace newness and lack the creativity needed to take the Internet to the next level. There needs to be a support for young talents for innovation to take place.
A lack of young people and drive has led to the failure to launch IPv6. It is not hard to find that recent RIR meetings have been attended solely by the same group of elderly professionals who have been in this industry for decades. While their contribution to the Internet is tremendous, it is also important for us to move forward by bringing in innovative and transformative ideas. We definitely need more energy in this industry.
Indeed, the Internet infrastructure industry may not be as profitable as the application business of the Internet, such as application and cryptocurrency. Young talents tend to go into these sectors for a better living. Meanwhile, as the Internet Infrastructure industry is still seemingly occupied by the "older professionals," this makes it even harder for young talents to enter this industry. Many young people are not even aware of the importance of Internet infrastructure, and relevant training and resources are limited. It is thus crucial for this industry to be innovative and to get rid of the image of being controlled by the "older folks" as a means to move forward.
LARUS understands the necessity of IPv6 as well as the importance of nurturing young talents. Along with the other firms, we provide IPv6 training and education. Furthermore, the LARUS Foundation, a government-recognized NGO founded in 2019 to promote education in Internet Governance and nurture the next generation of talents for a better Internet, has helped this cause. To date, we have educated over 10,000 students, and we hope to educate more in the years to come.
Looking to the future
The RIRs have two main functions, bookkeeper and distribution service of internet resources, one of which, the distribution service, have been largely obsolete due to exhaustion of the free pool of the internet resources.A redundant and half-functional marketplace was established 10 years ago; the policy of RIR and its guiding document is still very much centered around the distribution of the resources and does not towards a fair, transparent, and equal market.
The realization of the importance of the market and establishing a functional market space, recognizing the property ownership and center policy around protecting private property, and putting RIR in a sole bookkeeper position are desperate to happen.
Just last year, one of RIR, corrupted RIR AFRINIC was trying to endanger internet access of hundreds of million end users for their own corruption gains, and if it wasn't for the court of Mauritius, the internet will be left half-broken, and many users, including hospitals, airports, some key service of the internet will be disrupted and destroyed.
RIR's power needs to be regulated, regulators around the world should understand the existence of this marketplace for internet resources, and take away the power from RIR to create an internet that is fair, equal, and rules made by elected people of the public not just a few nerds in the IT space.
LARUS and many other brokers in the market are keen to make the market functional into a fair place for all companies; with its largest lease offering and a dynamic young team.LARUS is one of the few companies in the market place dedicating itself to innovation and helping small to mid-size business still have fair access the internet resources at an acceptable cost.
Without the innovation and creativity shown by LARUS and other like-minded innovators to create a better Internet for all, the current governance of the internet is in danger of failing in its’ basic function of uniting minds together for the promotion of humanity, It is for this reason that it is so important to challenge the status quo and vested interests that defend an outdated model of internet governance. Fairness and equality for all humanity depends on it.

